Preliminary Update on UAE Corporate Tax
SEPTEMBER 15, 2022
Please note that this is based on a general understanding of the consultation paper issued by the UAE Ministry of Finance and thus the points herein may change depending on the final law that will be issued. This is adapted from Document link: https://www.lexismiddleeast.com/news/2022-08-04_1
1. SNAPSHOT
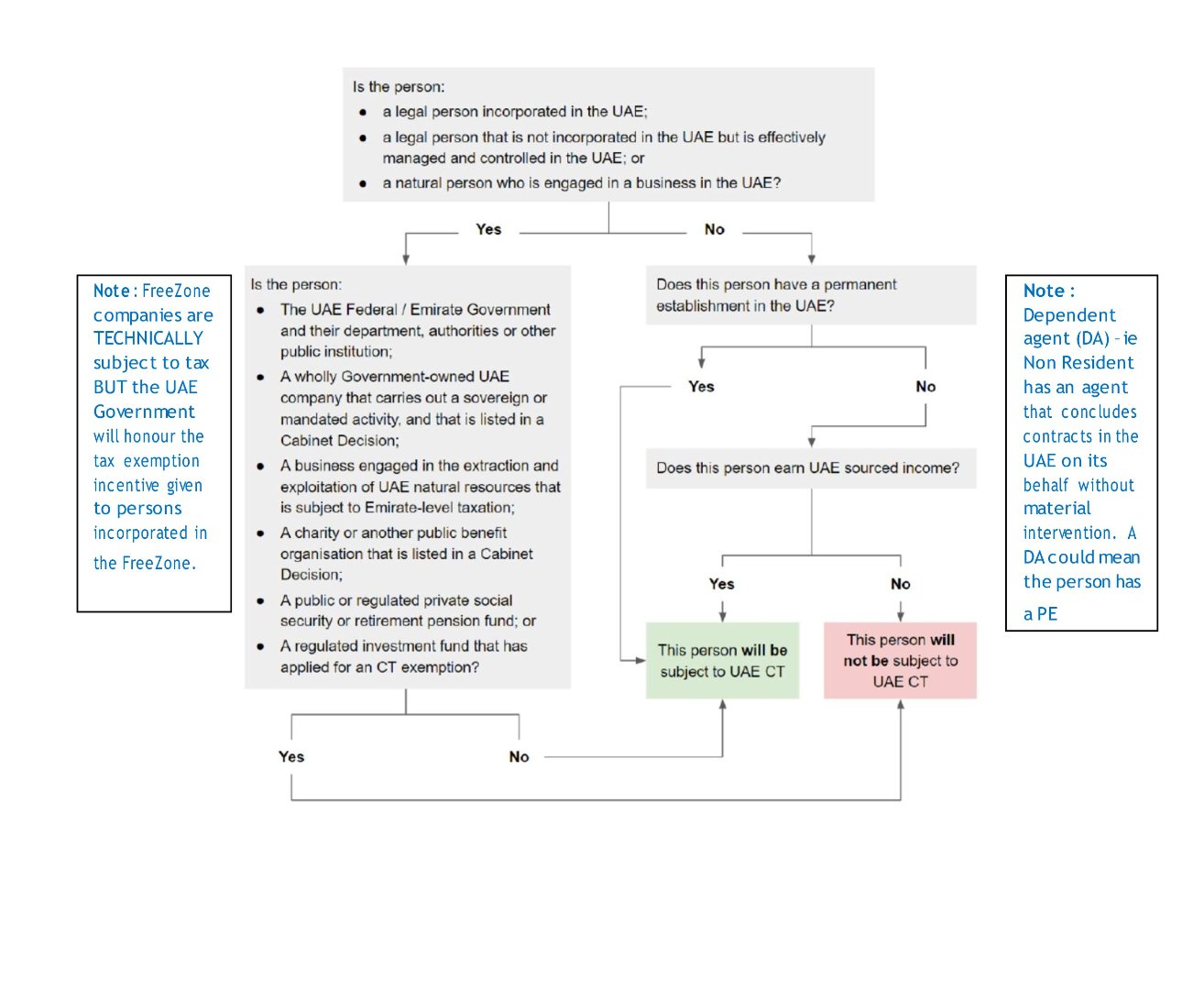
2.1 Basis of calculating taxable income
The Corporate Tax (CT) regime proposes to use the accounting net profit (or loss) as stated in the financial statements of a business as the starting point for determining their taxable income.
2.2 Treatment of unrealised gains and losses
Unrealised gains or losses arise in instances where an asset or liability held by a business has changed in value but no transaction to generate a gain or loss has yet taken place. For example, when a business property increases in value, but the property is not sold, the gain would be unrealised. These gains or losses may be recorded for accounting purposes even though they are not yet realised. The CT will have specific rules to determine whether an unrealised gain or loss should be taken into account when calculating taxable income. These relate to whether the gain or loss is related to capital items or revenue items.
2.3 Exempt income
UAE resident companies will be subject to CT on their worldwide income, including capital gains. However, to avoid instances of double taxation, the CT regime will exempt certain forms of income from taxation.
2.4 Exemption for dividends and capital gains
A UAE corporate shareholder will generally be exempt from CT on dividends received and capital gains earned from the sale of shares of a subsidiary company. Also, the proposed CT regime will exempt all domestic dividends earned from UAE companies. Dividends paid by foreign companies, and capital gains from the sale of shares in both UAE and foreign companies will also be exempt from CT, provided certain conditions are met.
2.5 Foreign branch profit exemption
A foreign branch would typically constitute a PE in the foreign country and be subject to CT (or an equivalent tax) on its profits in that foreign country. UAE companies can either (i) claim a foreign tax credit for taxes paid in the foreign branch country, or (ii) elect to claim an exemption for their foreign branch profits.
2.6 Expense deduction limitations
The calculation of taxable income will largely follow accounting rules, but the CT regime will disallow or restrict the deduction of certain specific expenses. This is to ensure that relief can only be obtained for expenses incurred for the purpose of generating taxable income, and to address possible situations of abuse or excessive deductions.
2.7 Interest capping rules
Interest and other similar financing costs are considered a cost of doing business and will accordingly be deductible for CT purposes. The proposed CT regime will cap the amount of net interest expense that canbe deducted to 30 percent of a business’ earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortisation (EBITDA), as adjusted for CT purposes.
Businesses may be allowed to deduct up to a certain amount of net interest expenditure (safe harbour or de minimis amount) irrespective of the interest deductibility limit based on the EBITDA rule. The interest capping rules will not apply to banks, insurance businesses, and certain other regulated financial services entities. Additionally, the interest capping rules will also not apply to businesses carried on by natural persons.
2.8 Non-deductible expenses
Businesses will be allowed to deduct up to 50 percent of expenditure incurred to entertain customers, shareholders, suppliers and other business partners, to acknowledge that these types of expenses often also have non-business or personal element.
2.9 Losses
A fundamental principle behind the CT regime is that CT is meant to be paid on the total profit of a business over its entire life cycle, as opposed to a single financial period. A business will be able to offset a loss incurred in one period against the taxable income of future periods, up to a maximum of 75 percent of the taxable income in each of those future periods. Tax losses can be carried forward indefinitely provided the same shareholder(s) hold at least 50 percent of the share capital from the start of the period a loss is incurred to the end of the period in which a loss is offset against taxable income. If there is a change in ownership of more than 50 percent, tax losses may still be carried forward provided the same or similar business is carried on by the new owners. No tax loss relief will be available for losses incurred before the effective date of CT.
3. GROUPS
Large businesses often conduct their operations through a group of companies, which has a parent company and a number of subsidiaries. The CT regime will allow full consolidation for tax purposes (tax grouping) for essentially wholly-owned groups of companies, and the transfer of losses between group companies that are 75 percent or more commonly owned.
3.1 Tax groups
A UAE resident group of companies can elect to form a tax group and be treated as a single taxable person if the parent company holds at least 95 percent of the share capital and voting rights of its subsidiaries.
3.2 Intra-group transfer of assets and liabilities
Intra-group transfer relief will be available for transfers of assets and liabilities between UAE resident companies that are at least 75 percent commonly owned, provided the assets and/or liabilities being transferred remain within the same group for a minimum of three years. Where intra-group relief is claimed, the relevant assets and liabilities will be treated as being transferred at their tax net book value, so that neither a gain nor a loss needs to be taken into account when calculating the taxable income of the transferor and the transferee company.
3.3 Restructuring relief
To facilitate mergers, spin-offs and other corporate restructuring transactions, the CT regime will exempt or allow for a deferral of taxation where a whole business, or independent parts of a business, are transferred in exchange for shares or other ownership interests.
4. TRANSFER PRICING
This section sets out the proposed treatment under the CT regime of transactions between related parties. The CT regime will have transfer pricing rules to ensure that the price of a transaction is not influenced by the relationship between the parties involved. In order to achieve this outcome, the UAE will apply the internationally recognised “arm’s length” principle to transactions and arrangements between related parties and with connected persons.
5. CALCULATION OF CT LIABILITY
5.1 Applicable CT rates
CT will be charged on the annual taxable income of a business as follows:
zero percent (0%) for taxable income not exceeding AED 375,000; and nine percent (9%), for taxable income exceeding AED 375,000.
5.2 Withholding tax
Given the position of the UAE as a global financial centre and an international business hub, a zero per cent
withholding tax will apply on domestic and cross-border payments made by UAE businesses.
5.3 Tax Credits
To avoid double taxation, the CT regime will allow a credit for the tax paid in a foreign jurisdiction against the CT liability on the foreign sourced income that has not been otherwise exempted. This is known as “Foreign Tax Credit”.
The maximum Foreign Tax Credit available will be the lesser of the amount of tax that was paid in the foreign jurisdiction; or the CT payable on the foreign sourced income.
6. ADMINISTRATION
6.1 Registration and deregistration
A business subject to CT will need to register with the FTA and obtain a Tax Registration Number within a prescribed period. Where a business ceases to be subject to the CT (e.g., due to cessation or liquidation of the business), it will need to apply to the FTA to be deregistered for CT purposes within three months from the date of cessation.
6.2 Filing, payment and refund
A business will only need to prepare and file one tax return and other related supporting schedules with the FTA for each tax period. Each tax return and related supporting schedules will need to be submitted to the FTA within nine months of the end of the relevant Tax Period. Payments to settle a taxpayer’s CT liability for a Tax Period will need to be made within nine months of the end of the relevant Tax Period. Where a taxpayer can demonstrate that a CT refund may be due, the taxpayer can apply to the FTA to request a refund.

